Problem 235: Find the length of the curve defined by
(1) ![]()
from ![]() to
to ![]() .
.
Solution: The length of a curve is given by
(2) ![]()
That is,
(3) 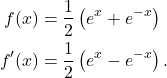
Then
(4) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{align*} L & = \int_{a}^{b} \sqrt{1+[f'(x) ]^2} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \sqrt{1+\left( \frac{1}{2}e^x-\frac{1}{2}e^{-x}\right)^2} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \sqrt{\left(\frac{e^x}{2}-\frac{e^{-x}}{2} \right)^2 +1} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \sqrt{(\sinh x)^2 + 1} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \sqrt{\cosh^2 x} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \cosh x \ dx \\ & = \sinh x \bigg|_{0}^{1} \\ & = \frac{e^{-x}(e^{2x}-1)}{2}\bigg|_{0}^{1} \\ & = \frac{e^1(e^2 - 1)}{2} - \frac{e^0(e^0-1)}{2} \\ & = \frac{e^1-e^{-1}}{2}.\end{align*}](https://1problematatime.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9dedc0e7e6cdea9f6346882c8253be1b_l3.png)
That is, the length of the curve between 0 and 1 is
![]()

Problem 235: Find the length of the curve defined by
(1) ![]()
from ![]() to
to ![]() .
.
Solution: The length of a curve is given by
(2) ![]()
That is,
(3) 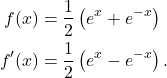
Then
(4) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{align*} L & = \int_{a}^{b} \sqrt{1+[f'(x) ]^2} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \sqrt{1+\left( \frac{1}{2}e^x-\frac{1}{2}e^{-x}\right)^2} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \sqrt{\left(\frac{e^x}{2}-\frac{e^{-x}}{2} \right)^2 +1} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \sqrt{(\sinh x)^2 + 1} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \sqrt{\cosh^2 x} \ dx \\ & = \int_{0}^{1} \cosh x \ dx \\ & = \sinh x \bigg|_{0}^{1} \\ & = \frac{e^{-x}(e^{2x}-1)}{2}\bigg|_{0}^{1} \\ & = \frac{e^1(e^2 - 1)}{2} - \frac{e^0(e^0-1)}{2} \\ & = \frac{e^1-e^{-1}}{2}.\end{align*}](https://1problematatime.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9dedc0e7e6cdea9f6346882c8253be1b_l3.png)
That is, the length of the curve between 0 and 1 is
![]()
Leave a Reply