Problem 125: Calculate ![]() of
of
(1) ![]()
Solution: We have two different options to find the derivative of (1). First, I will expand the logarithm using properties of logarithm. Then I will find the derivative and evaluate. That is,
(2) 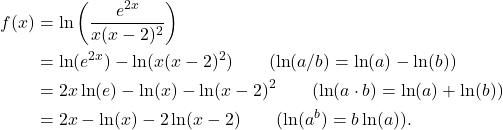
Hence,
(3) 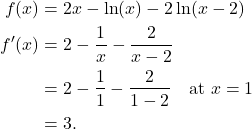
Therefore, ![]() .
.

Leave a Reply